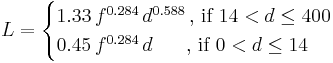Weissberger's model
Weissberger’s modified exponential decay model, or simply, Weissberger’s model, is a radio wave propagation model that estimates the path loss due to the presence of one or more trees in a point-to-point telecommunication link. This model belongs to the category Foliage or Vegetation models.
Contents |
Applicable to/under conditions
- This model is applicable to the cases of line of sight propagation. Example is microwave transmission.
- This model is only applicable when there is an obstruction made by some foliage in the link. i.e. In between the transmitter and receiver.
- This model is ideal for application in the situation where the LOS path is blocked by dense, dry and leafy trees.
Coverage
Frequency: 230 MHz to 95 GHz[1]
Depth of Foliage: up to 400 m
History
Formulated in 1982, this model is a development of the ITU Model for Exponential Decay (MED).
Mathematical formulation
Weissberger’s model is formally expressed as
where,
L = The loss due to foliage. Unit: decibels (dB)
f = The transmission frequency. Unit: gigahertz (GHz)
d = The depth of foliage ‘’’along’’’ the path. Unit: meters (m)
Points to note
- The equation is scaled for frequency specified in GHz range.
- Depth of foliage must be specified in meters (m).
Limitations
- This model is significant for frequency range 230 MHz to 95 GHz only, as pointed out by Blaunstein.
- This model does not define the operation if the depth of vegetation is more than 400 m.
- This model predicts the loss due to foliage. The path loss must be calculated with inclusion of the free space loss.[2]
References
- ^ Radio propagation in cellular networks, N. Blaunstein
- ^ Introduction to RF propagation, John S. Seybold
Further reading
- Introduction to RF Propagation, John S. Seybold, 2005, John Wiley and Sons.
- Radio Propagation in Cellular Networks, N. Blaunstein, 2000, Artech House
- The Mobile Radio Propagation Channel, J. D. Parsons, 2000, Wiley
- Mark A. Weissberger (1982) (PDF). An initial critical summary of models for predicting the attenuation of radio waves by trees. http://stinet.dtic.mil/oai/oai?&verb=getRecord&metadataPrefix=html&identifier=ADA118343. Retrieved 2007-02-21.